Knowledge Based Authentication (KBA)
Knowledge Based Authentication (KBA) requires the cardholder to verify their identity, based on information only they should know. For example, if they are asked a security question, such as "What was your first pet's name?", they can enter the answer "Snuffles". The answer can then be checked against the answer stored for the card.
You enrol the card in KBA using the 3D Secure service and provide the security question ID and answer pair. Thredd provides the Access Control Server (ACS)![]() A system used to manage the 3D Secure authentication service for the issuer. During an authentication session, the ACS communicates with the Card Scheme and Thredd systems, and may also interact with the cardholder, by providing Challenge screens. with the security question to use for KBA. During the e-commerce authentication session the ACS asks the cardholder to answer the security question and then sends a KBA authentication request to Thredd together with the cardholder’s answer. Thredd compares the answer returned by the ACS to the answer stored in the Thredd database and then returns a response to the ACS. KBA is typically combined with OTP SMS: the cardholder is first asked to authenticate using OTP and then via KBA.
A system used to manage the 3D Secure authentication service for the issuer. During an authentication session, the ACS communicates with the Card Scheme and Thredd systems, and may also interact with the cardholder, by providing Challenge screens. with the security question to use for KBA. During the e-commerce authentication session the ACS asks the cardholder to answer the security question and then sends a KBA authentication request to Thredd together with the cardholder’s answer. Thredd compares the answer returned by the ACS to the answer stored in the Thredd database and then returns a response to the ACS. KBA is typically combined with OTP SMS: the cardholder is first asked to authenticate using OTP and then via KBA.
KBA is considered a type of two-factor authentication, since it requires a secondary verification method through a separate communication channel to that in which the primary verification takes place. This secondary verification is obtained via knowledge questions. It is also considered a form of Strong Customer Authentication (SCA), which is a requirement of the Second Payment Services Directive (PSD2).
The figure below provides an overview of the cardholder authentication process during a transaction, using KBA.
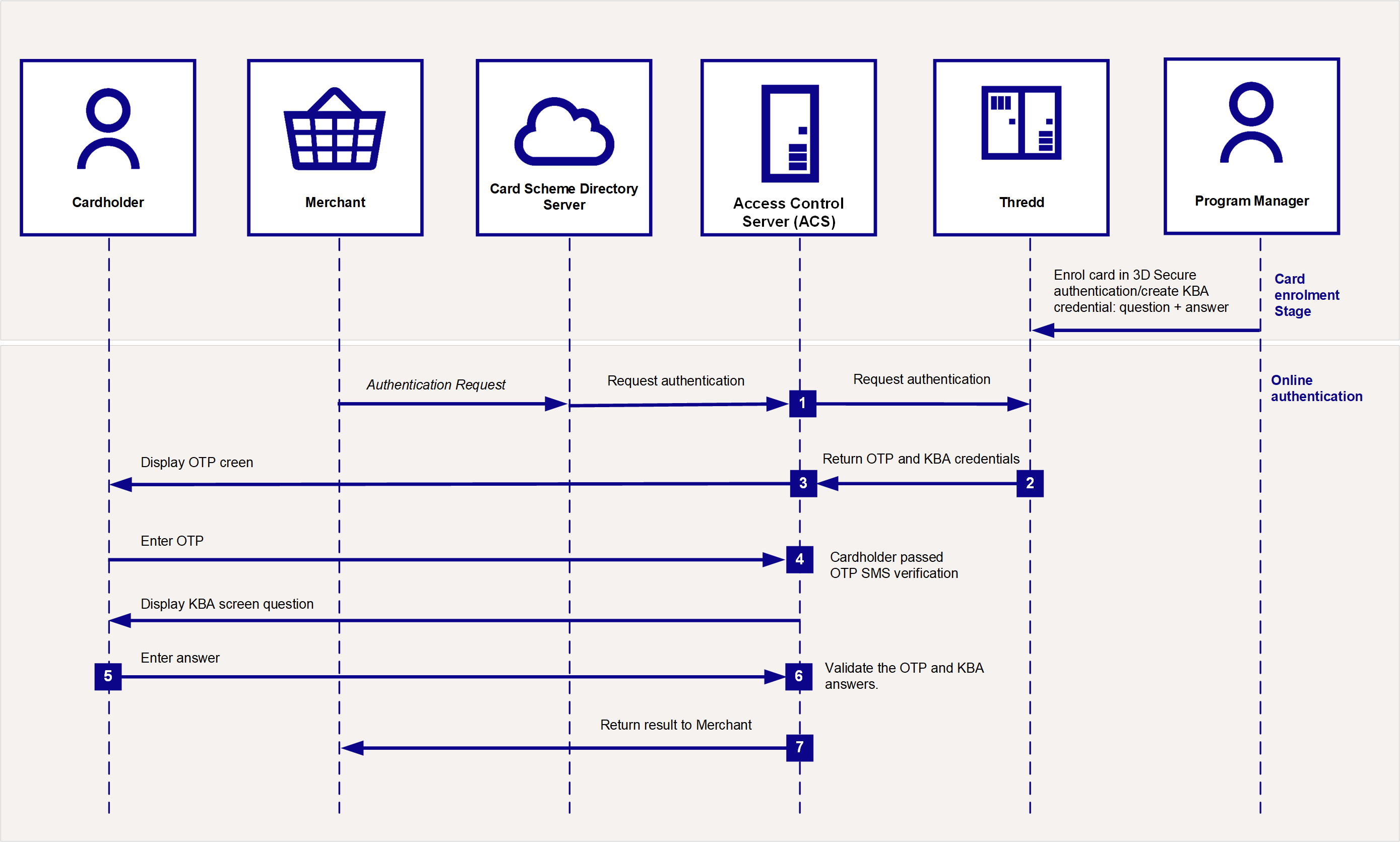
Figure: Knowledge Based Authentication Call Flow
Prior to using KBA, you need to set up the KBA credential, including the question and answer pairs to be used for the card during a KBA authentication session.
An online authentication session using KBA is typically combined with OTP SMS. The KBA authentication follows directly after successful OTP SMS authentication.
-
The ACS connects to Thredd in real-time to query the types of authentication the card is registered for (e.g., OTP SMS and KBA).
-
Thredd replies with the OTP and KBA challenge profile configured for your product.
-
The ACS follows the process for OTP SMS, presenting the OTP screen to the customer, who enters the OTP which Thredd sends to their mobile phone via SMS.
-
Following OTP authentication, the ACS presents an additional screen to the cardholder, asking them to answer the security question(s) set up for their card.
-
The cardholder enters their answer(s).
-
The ACS validates the OTP and KBA answers.
-
The ACS confirms whether authentication has been successful or not.
What happens after authentication?
Once the cardholder is authenticated, the merchant can proceed with requesting authorisation for the transaction. (The merchant acquirer includes the 3DS secure value they receive from Cardinal within the transaction: UCAF field.)
Thredd validates the 3DS key for a Mastercard transaction (for Visa, Visa generates the key and validates it).
Depending on your External Host Interface (EHI) mode, Thredd approves/declines the transaction or sends to your EHI endpoint to approve or decline.
You can view details of your 3D Secure transactions in the 3D Secure Portal.
For more information, refer to the 3D Secure Guide (Apata) or 3D Secure Guide (Cardinal).