1.5 Card Payment Networks
Thredd supports cards enabled for use on Visa, Mastercard and Discover networks, as well as smaller networks that use the Mastercard Network Exchange![]() Enables smaller networks to use Mastercard as a routing platform for payments. Can also be referred to as MNEX or MNGS. (MNE), such as STAR and Pulse1. These global card payment networks are operated by Card Scheme organisations, which regulate and manage activity on their networks. The payment networks are open to financial institutions and processors, and allow cardholders to pay with Scheme-issued cards and merchants to accept card payments in their businesses worldwide. Thredd operates on the card Issuing side, acting as the gateway between the Card Schemes and the card issuers/Program Managers.
Enables smaller networks to use Mastercard as a routing platform for payments. Can also be referred to as MNEX or MNGS. (MNE), such as STAR and Pulse1. These global card payment networks are operated by Card Scheme organisations, which regulate and manage activity on their networks. The payment networks are open to financial institutions and processors, and allow cardholders to pay with Scheme-issued cards and merchants to accept card payments in their businesses worldwide. Thredd operates on the card Issuing side, acting as the gateway between the Card Schemes and the card issuers/Program Managers.
The payment networks are highly standardised and strictly regulated, so interested parties must be certified to be able to participate. Thredd is a certified Issuer Processor, which enables us to process various types of card payment transactions from the payment networks we support. Thredd transforms messages from payment networks and other sources into a simplified and unique internal format, available via EHI. Integrating to EHI enables you receive all Thredd supported payment network messages.
EHI content is evolving with the changes introduced by the Card Schemes via periodical releases and ad-hoc announcements. Thredd provides you with notifications of these changes and new EHI version releases.
1.5.1 Card Payment (Network) Transactions
In regions which support the Dual Message System (e.g., UK, Europe and Australia) there are two main steps in a typical card payment transaction:
Step 1: Request for Authorisation
The card scheme sends an authorisation request to Thredd. Thredd receives the authorisation request via the network and responds in realtime after checks done by Thredd and your systems. The result may be approval or decline.
-
An approved authorisation does not move any funds, but only blocks/unblocks the authorised amount. Approved authorisations are normally cleared later by financial message to finalise the transaction. If the financial message does not arrive in a defined period, the block is removed.
-
Some messages such as balance enquiries are also Authorisation messages, but there are no complementary financial messages for those messages.
Step 2: Financial/Clearing Message
The card scheme sends a financial (or clearing) message to Thredd. Most common financial messages are presentments, which mostly match with an authorisation received previously. Financial messages require a change to the actual balance of the cardholder account. If there is a linked authorisation, financial message must clear the blocking applied for the matching authorisation.
Note that the authorisation amount and financial amount may differ, and blocked amount actual balance mechanisms should ideally be managed independently.
In the life-cycle of a transaction, there may be several financial messages. These messages include chargebacks for disputed financial transactions and reversals of presentments and chargebacks. The figure below lists possible message types and their phases and orders in a transaction life cycle.
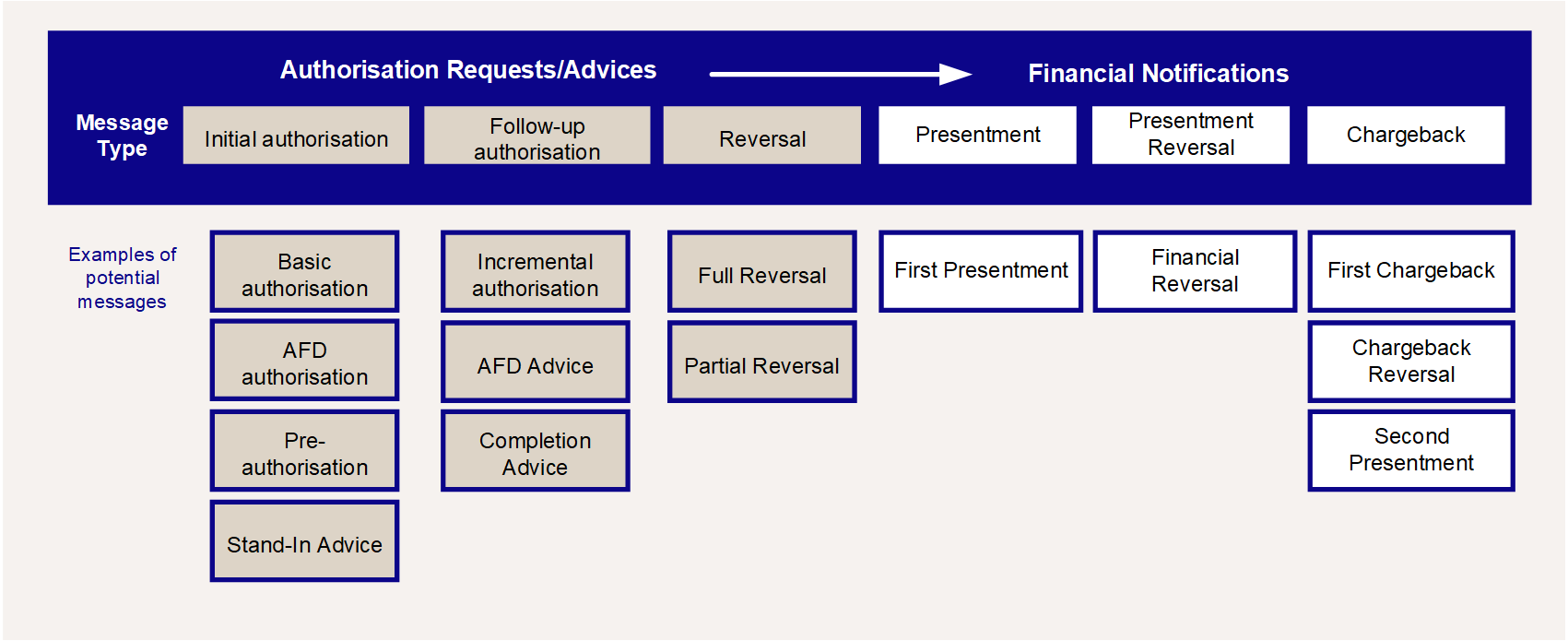
Figure 7: Examples of typical authorisation and financial messages - Dual Message Systems
Most transaction life-cycles consist of a single authorisation and first presentment. However, there are more complex combinations that needs to be supported by EHI. For more information on the transaction types and the steps in processing, see Transaction Flow Scenarios - Dual Message Systems.
1.5.2 Non-Card-Network Transactions
These are transactions that are not originated via the payment networks we support, but by another means, such as Web Services and BACS, CHAPS or Faster Payments. Examples include: load of funds into an account, payments to an account via Faster Payments or card expiry notifications.